VOCs are the abbreviation of volatile organic compounds. There are several definitions, for example, the United States ASTM D3960-98 standard defines VOC as any organic compound that can participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions. The definition of the US Federal Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Volatile organic compounds are carbon compounds that participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions except CO, CO2, H2CO3, metal carbides, metal carbonates, and ammonium carbonate. The World Health Organization (WHO, 1989) defines total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs) as the general term for volatile organic compounds that have a melting point below room temperature and a boiling point between 50 and 260°C. The international standards ISO 4618/1-1998 and the German DIN 55649-2000 standard for the general term color paints and varnishes define VOCs as, in principle, any self-extracting organic liquids and/or solids under normal temperature and pressure. . At the same time, the German DIN 55649-2000 standard, when it comes to the determination of VOC content, makes a limitation that any organic compound with a boiling point or initial boiling point lower than or equal to 250°C under normal pressure conditions. BASF believes that the most convenient and common method is to define which substances belong to VOCs based on boiling points, and the most common consensus is that VOCs refer to those chemicals whose boiling points are equal to or lower than 250°C. Therefore, those whose boiling points exceed 250°C are not classified as VOCs and are often referred to as plasticizers.
These definitions have the same place, but they also have their own emphasis. As defined by the United States, there is no limitation on the boiling point of the initial boiling point, emphasizing participation in atmospheric photochemical reactions. Those who do not participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions are called exempt solvents such as acetone and tetrachloroethane. The World Health Organization and BASF have limited the boiling point or the initial boiling point, regardless of whether they participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions. The international standard ISO 4618/1-1998 and the German DIN 55649-2000 standard do not limit the boiling point of the initial boiling point. Whether or not they participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions, they only emphasize the ability to self-generate under normal temperature and pressure.
The definition of these VOCs can be divided into two categories. One is the VOC definition in the ordinary sense, which only shows what is volatile organic compounds, or under what conditions is volatile organic compounds; the other is the definition of environmental protection, In other words, it is the kind of volatile organic compounds that are active, that is, the types of volatile organic compounds that can cause harm. It is very obvious that from an environmental point of view, it is very important to volatilize and participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions. Non-volatile or not participating in atmospheric photochemical reactions does not pose a hazard. This is also the reason why Europe classifies solvents by the potential for actinic ozone production.
According to WHO's definition, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) refer to various organic compounds with boiling points of 50°C to 260°C at room temperature. According to its chemical structure, VOCs can be further divided into alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons, esters, aldehydes, and others. More than 300 types have been identified so far. The most common are benzene, toluene, xylene, styrene, trichloroethylene, trichloromethane, trichloroethane, diisocyanate (TDI), diisocytotoluene ester, and the like.
Formaldehyde is also a volatile organic compound, but formaldehyde is easily soluble in water and is different from other volatile organic compounds. It has a wide range of indoor sources and a high release concentration. Therefore, formaldehyde and other volatile organic compounds are often described separately.
In addition to formaldehyde, the vast majority of volatile organic compounds are generally insoluble in water and readily soluble in organic solvents. In the room, their respective concentrations are often not very high, but when several VOCs co-exist in indoor air, their joint action cannot be ignored. Due to their large variety and low concentration of individual components, TVOC is often used to represent the total amount of volatile organic compounds in the chamber. TVOC is a measure of interior furnishings such as interior decoration and furniture in buildings. An important indicator of the degree of influence on indoor air quality.
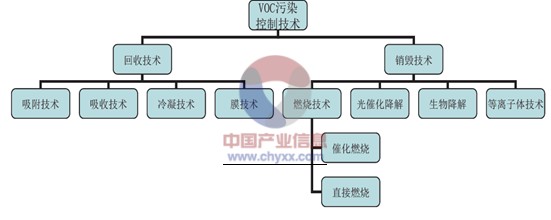
Commonly used VOCs control technology
Window._bd_share_config={"common":{"bdSnsKey":{},"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"32"},"share":{},"image":{"viewList":["qzone","tsina","tqq","renren","weixin"], "viewText":"Share to:","viewSize":"16"},"selectShare":{"bdContainerClass":null,"bdSelectMiniList":["qzone","tsina","tqq","renren" ,"weixin"]}};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')).src='http://bdimg.share. Baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];
X-Ray Fim Envelopes,Medical Film Envelope,X Ray Manila Envelope,Film Purpose Envelope
Sun Kee Envelopes Limited , https://www.sunkeeenvelope.com